Osteochondrosis is one of the most common spinal pathologies.In this disease, the tissue of the spine cartilage and intervertebral discs is affected.Most often, osteochondrosis affects the lumbar region, as it is in it that the maximum load when walking, sitting, running and other activities.
If treatment does not start in time, then the disease can lead to radiculus, intervertebral hernia, lumbago, Ishias, disability.
Stages of development
The disease is usually divided into several stages:
- First stage- There are minor changes in the intervertebral discs, the spinal column is not deformed, a person feels minor pain in the lower back.
- Stage 2- Pain in the affected area becomes stronger, violations in the intervertebral discs become more noticeable.
- Stage 3- There is intervertebral hernia, the spinal column is deformed.The patient feels severe pain in the affected area.
- Stage 4- It becomes difficult for a person to walk and make any movement.The pain appears in slight movement.At this stage, the latter is given the patient as a rule.
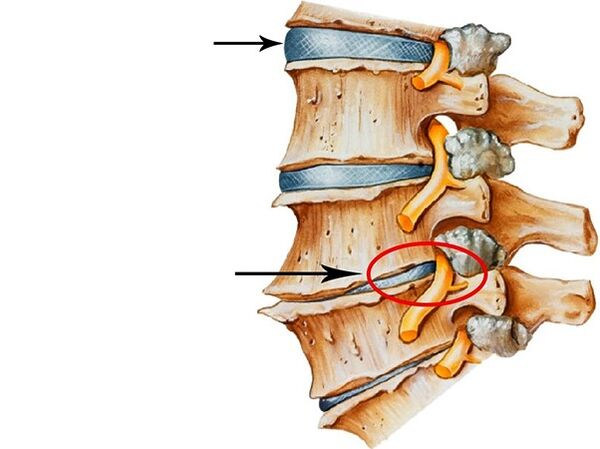
Causes
Most often, people, the profession or type of activity of which are accompanied by physical exercises and large loads in the lumbar department: builders, motors, service workers and athletes undergo osteochondrosis.Also, pathology can occur to teachers, cashiers, office workers, as they spend most of their time in a sitting position.
There are many factors that affect the emergence of osteochondrosis:
- Lack of physical exercise, performing a sedentary lifestyle.
- Strong load in the middle region.
- Diseases of the joints and spine.
- Injuries to the middle spine.
- Flat feet or club.
- Overweight
- Disordishes Poster, Stoop.
- Scoliosis or kyfosis.
- Long -term hypothermia.
- Age -related changes in the back.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Some internal diseases of cardiovascular, nervous, endocrine systems.
- Improper food.
Symptoms
The main signs of lower back osteochondrosis are:
- Severe painful pain in the lower back, sometimes giving up on the leg and intensifying when you perform any movement, sneezing, coughing, etc.
- Continuous tension of the back muscles.
- The inability to fix the back after a long stay in the same position.
- Unpleasant sensations when sloping or stretching of the back.
- Lights at the bottom of the back.
- Loss of sensitivity in buttocks, hips.
- Goosebumps, a sensation of sensitivity in the leg.
- Numbness of the legs and legs.
- The constant coldness of the legs and the feeling of cold on the feet.
- Varicose veins.
- Violation of power in men.
- Irregular menstruation in women.
The main symptom of pathology is the pain when the appearance of which you should urgently consult a doctor.
Troubleshooting
The diagnosis of osteochondrosis begins with a thorough examination of the patient and collecting an anamnesis - the doctor asks the patient about cases of osteochondrosis in sex, chronic illnesses, lifestyle, type of activity, common diseases and spine.
Further, the specialist describes the instrumental diagnostic methods, among which:
- X -Ray of the lumbar region- allows you to discover the presence of pathology and the degree of vertebral damage.
- Calculated Tomography (CT)- A more accurate research method that allows you to determine the damage to the intervertebral discs, the degree of change, the degree of deformation of the spine.
- MRI- allows you to fully study the intervertebral discs, gives information about minor disorders in the back, is used in difficult cases or if the exam photography using CT or X -Rray examination is blurred.
- Myelography- a type of diagnosis in which a contrast agent is used to detect intervertebral hernias.
Based on the data, the specialist determines the degree of pathology and describes the necessary treatment.
Treatment
The treatment of osteochondrosis is performed comprehensively.The necessary medicines and procedures are prescribed only by a physician, strictly individually.
First of all, the patient is prescribed a number of drugs based on NSAID -Non -inflammatory non -steroidal that can relieve inflammation and eliminate pain in the affected area.Chondroprotectors are also prescribed - medicines that stop the process of destruction of cartilage and food tissue.Vitamins that improve the condition of the whole organism are described as additional medicines.
For many spinal diseases, including osteochondrosis, physiotherapy is prescribed.Procedures are able to improve blood circulation in lesions, relieve tension from the muscles, eliminate pain and inflammation.With osteochondrosis, electrophoresis, acupuncture, magnetic therapy and other procedures are prescribed.
The patient is also prescribed massage, mud baths or hydrotherapy with which it is possible to ease the tension and fatigue of the muscles, to calm them down and to increase blood flow.Mud muddy baths can eliminate the inflammatory process.
In the early stages of the disease, exercise therapy is prescribed - a colorful gymnastics, whose performance helps to restore the movement of the spine, to strengthen the back muscles.In stages 3 and 4 of osteochondrosis, this type of treatment is not used.
Diet is very important in the treatment of the disease - it is necessary to include in diet products rich in minerals - fruits, vegetables, porridge.Make sure you eat low meat, as it is rich in protein - it will be more useful to eat chicken or rooster.It will be useful to use fermented dairy products.It is recommended to reduce the amount of fatty, sharp, smoked, fried dishes.It is important to observe the way of drinking - be sure to drink at least 1 liter of clean water a day.
With osteochondrosis of the lumbar region, treatment in a sanatorium will be useful, where experts throughout the patient's stay in the complex will treat the disease, and the patient is constantly under the supervision of doctors.
If conservative treatment methods do not help, then the surgical treatment method is used.During surgery, the affected wheels or cartilage are replaced by an implant.And if there is an intervertebral hernia, then it is removed.
PREVENTION
- Limit the load on the lower back.
- Play sports, do morning exercises.
- Eat straight.
- Try to prevent damage to the lumbar spine.
- Avoid lower back hypothermia.
- With a long place, change your body position more often, get up regularly and do simple exercises for warm or just walk.
- Save the right behavior, don't keep.
- In case of club or flat legs, wear special orthopedic layers that reduce the load on the back.

















































